Applications:
|
|
Features:
|
|
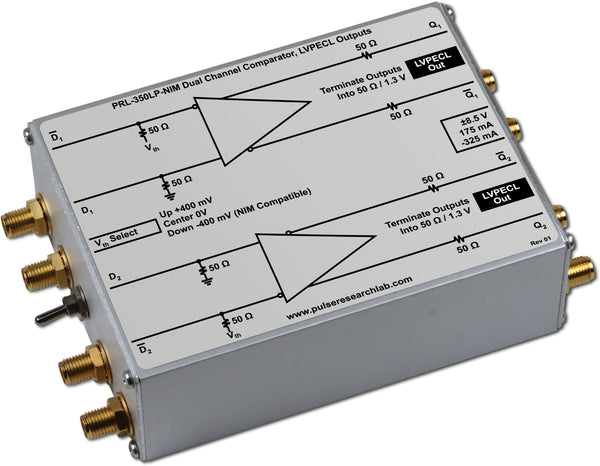
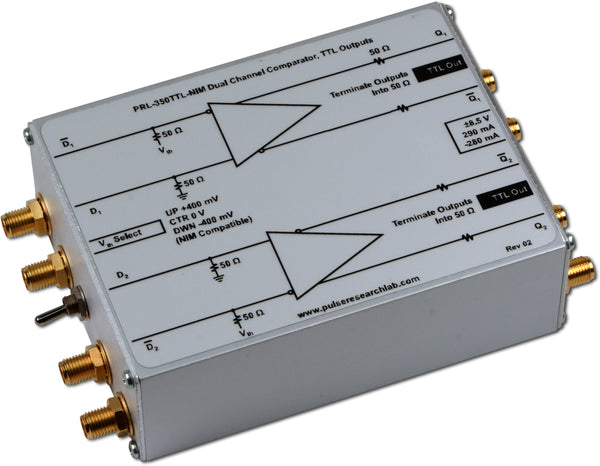
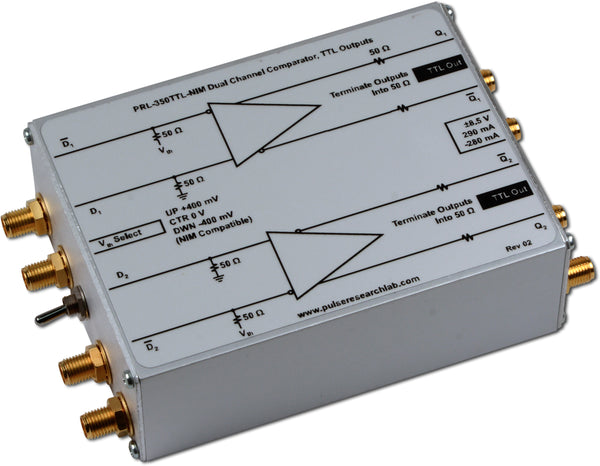
DescriptionThe PRL-350NIM is a high-speed dual-channel comparator modules with complementary 0 V to -800 mV NIM outputs. The PRL-350NIM is designed for driving 50 Ω transmission lines terminated to 50 Ω. All outputs of the PRL-350NIM are 50Ω back terminated and must be terminated into 50Ω for optimum performance. The input threshold voltage can be selected either from a set of preset values of +50 mV, 0 V or 50 mV using a common three-position switch, or varied independently in each channel by applying a DC voltage to one of the two inputs. Input Common Mode Range is -2.0 V to +3.0 V. The input threshold voltage can also be varied independently in each channel by applying an external DC bias voltage or shunt resistor to the D input.
These high speed comparators are Mini Modular Instruments ™ that can be used as peak detectors, threshold detectors, sine wave to square wave converters, window comparators or differential line receivers, etc. Typical minimum input voltage required at 150 MHz is 10 mVPP into 50 Ω. Each unit is supplied with a ±8.5 V AC/DC Adapter and housed in an attractive 1.3 x 2.9 x 3.9-in. extruded aluminum enclosure. |
 Fig. 1 PRL-350NIM Block Diagram
Fig. 1 PRL-350NIM Block Diagram(0° C ≤ TA ≤ 35° C)*
Unless otherwise specified, dynamic measurements are made with all outputs terminated into 50 Ω.
| Symbol | Parameter | PRL-350NIM | Unit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Typ | Max | |||
| RIN | Input Resistance | 49.5 | 50.0 | 50.5 | Ω |
| ROUT | Output Resistance | 49.5 | 50.0 | 50.5 | Ω |
| VTH+ | Preset positive threshold voltage | 49.5 |
50.0 | 50.5 |
mV |
| VTH- | Preset negative threshold voltage | -50.5 |
-50.0 |
-49.5 |
mV |
| VTH0 | Preset zero threshold voltage(1) | -10 |
0 | 10 |
mV |
| VOL | Output Low Level | -875 |
-800 |
-775 |
mV |
| VOH | Output High Level | -50 |
0 |
50 |
mV |
| IDC1 | DC Input Current, +8.5 V | 20 |
30 |
mA | |
| IDC2 | DC Input Current, -8.5 V | -275 |
-265 |
mA | |
| VDC1 | DC Input Voltage, +8.5 V | 7.5 | 8.5 | 12.0 | V |
| VDC1 | DC Input Voltage, -8.5 V | -12.0 | -8.5 | -7.5 | V |
| VAC1 | AC/DC Adapter Input Voltage, 120 VAC | 103 | 115 | 127 | V |
| VAC2 | AC/DC Adapter Input Voltage, 220 VAC | 206 | 230 | 254 | V |
| tPLH | Propagation Delay to output↑ | 1.5 |
ns | ||
| tPHL | Propagation Delay to output↓ | 1.5 |
ns | ||
| tr/tf | Rise/Fall Times, 10% - 90% | 450 |
550 |
ps | |
| tSKEW | Skew between any 2 outputs | 450 |
650 |
ps | |
| Vin I | Minimum Input Voltage @ 150 MHz(2) | 20 | 10 | mVPP | |
| Vin II | Minimum Input Voltage @ 250 MHz(2) | 40 | 20 | mVPP | |
| VCM | Input Common Mode Range | -2.0 | +3.0 | V | |
| fmax | Max. Clock Frequency | 300 |
330 |
MHz | |
| Size | 1.3 x 2.9 x 3.9 | in. | |||
| Weight, w/o AC adapter | 7 | Oz | |||
| Shipping weight, w/AC adapter | 4 | lb | |||
(1) If the switch is set to the center position (0 V threshold) a non-driven channel may oscillate and induce jitter in the driven channel. Connect any output to any input to stop the oscillation.
(2) In order to reduce jitter near fMAX, terminate the non-driven input into 50 Ω when the input voltage is less than 20 mVPP.